Experiments
AGV-BASED PRODUCTION LINE FOR MORE FLEXIBLE MANUFACTURING IN THE TEXTILE INDUSTRY (AGVFLEXTEX)
Republic of Serbia (Vojvodina and Central Serbia)
![]() Laboratory of ideas – iDEAlab
Laboratory of ideas – iDEAlab
Experiment objective
The main wider objective of this project is to create benefits for consortium members that aligns with and supports their strategic goals, as well as benefits for the entire regional sector of the garment industry and technology providers.
The specific objectives for the IVKOVIC doo, the Serbian company specialized in designing and creating high class woven and knitted garments for the woman will be:
- transformation of the labour-intensive production system into a flexible production system through collaboration of AGVs with workers in the existing production system layout.
- visualization of material flows through the production system and creation of real-time data flows using the batch RFID labelling, enabling efficient organization, monitoring and management of production processes.
- realization of planned digital transformation activities (according to the concept defined by the DIH) in a way that they will be fully operable beyond the pilot stage, considering them only as the first stage towards the creation of a fully smart production system.
The specific objective for the iDEAlab, one of several Serbian DIHs, will be to prove its capability to fully operate in one-stop-shop manner related to digital transformation of production and logistic processes, thus maturing into a regional marketable multi-partner collaborative platform.
Challenges
IVKOVIC doo (or IVKO Woman) comes from the garment industry that is characterized by labour-intensive activities. Over the past decade, several key trends have emerged that have reshaped the way the garment and textile industry is organized. Company must assess the impact of these trends on their strategic and operational plans. The main challenges that are addressed with this project are:
- Challenge 1: Lean retailing – retailers shift as much as logistics activities as possible to the upstream value chain members (garment manufacturers) in order to achieve their efficient flow of goods (low level of inventory, high service level). In such circumstances, manufacturers are under the pressure to take responsibility for entire logistics and delivery, stock management or in one word “full service”. This requires manufacturers to have a high level of production efficiency and real-time coordination and collaboration with all value chain members if they want to remain competitive.
- Challenge 2: Speed to market – fast turnovers in styles and fashion trend affect the shorter product lifespan, so garment manufacturers must be able to respond to a range of small, irregular orders, which would only be possible in case of efficient, flexible and agile production system and related logistics activities.
- Challenge 3: Digitalization of the production planning, balancing and control – digitalization supported by the automation of the material flow (based on AGV solution) to boost flexible products making with lover production lead time and better overall production resources utility.
- Challenge 4: Shifting company from “analog” mindset – integration of innovative digital technologies into SMEs production system assumes their mental shift to adopt these innovative approaches.
Challenge 5: Production layout challenges – Appropriate restructuring of production line and material flows within the given facility boundaries.
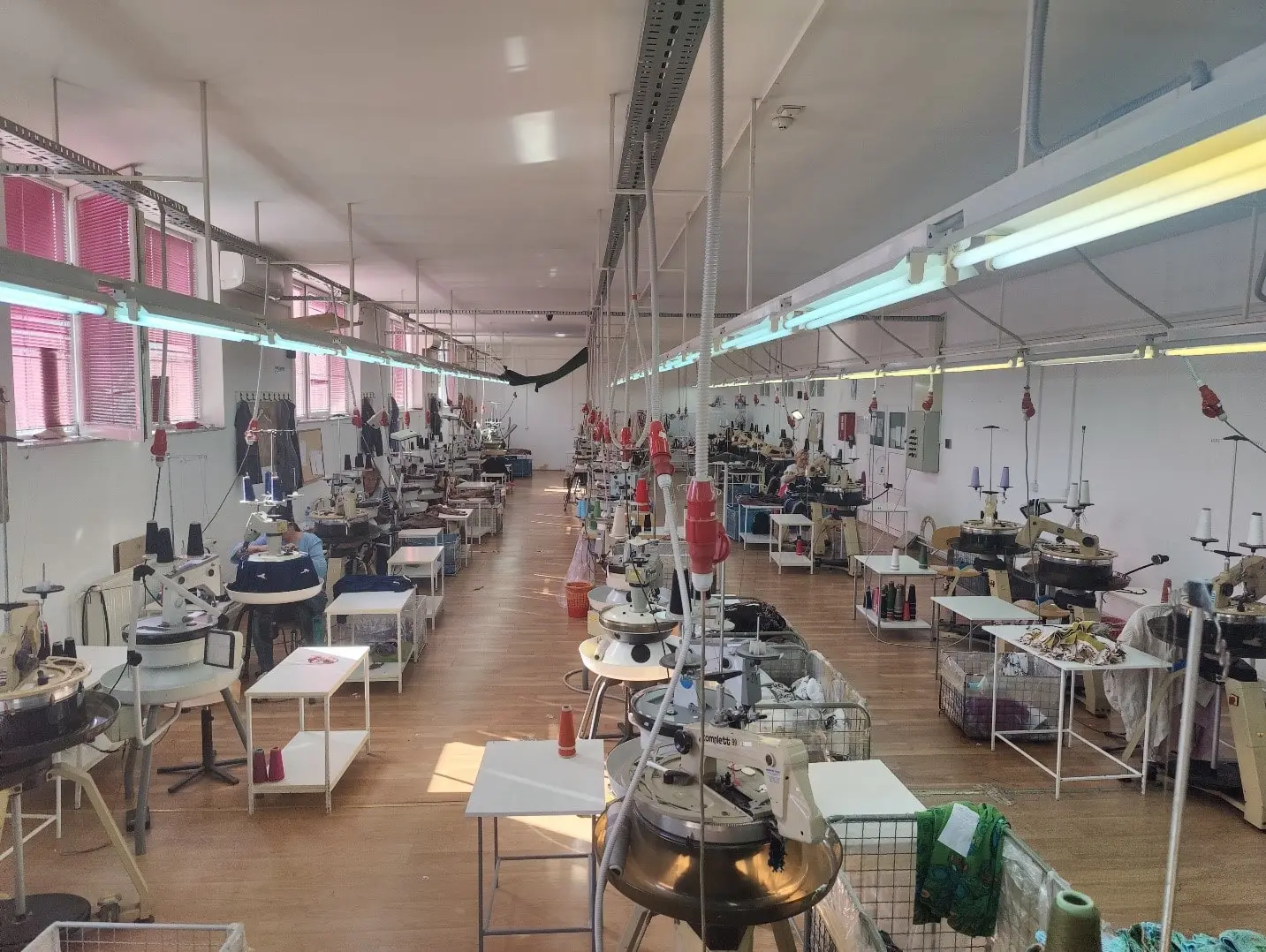

Current state of the production organisation
Implementation Solution
Bering in mind that companies are approaching the digitalization of their manufacturing operations in phases, such as: (1) the development of a connected, then (2) transparent, and finally (3) intelligent production system, it can be said that our experiment includes the first two phases. That is, this experiment covers digitalization of the production system and automation of the material flow through the production system, establishing basic connection of machines, material, people and other resources in order to collect real-time data required for creating optimal decision-making in production. Beyond the scope of this project is the final phase of creating intelligent production system that will have the power for fully autonomous decision making. The activities related to planning, organization, management and control of the production system will be the subject of a kind of Manufacturing execution system (MES), based on IoT, AGV and data analytics technology, that will serve for production planning and scheduling (balancing), job control and production performance monitoring. The following Figure presents the experiment concept that shows involved technology (robotics, IoT, data analytics), the manufacturing planning and control principles and recommended implementation diagram (path).
Tanks, counted from decades to hundreds, are usually 2,5m height with a 3m diameter and they are usually located in rural areas. Thus, technicians and quality experts have to travel by car, use a ladder, climb won the top and take samples from every tank or use (Do-It-Yourself) handheld devices to measure and document the pH and salinity levels. TOFIoT will deploy more than 30 sensors to remotely monitor the fermentation conditions within at least 15 tanks in a safe, reliable and digital way. In this case, sensors will transfer their measurements to the attached IoT node and the node will wirelessly transfer them either to the network’s gateway (6LoWPAN version) or directly on Cloud (NBIoT version).
TOFIoT partners have the complementary expertise to make this digital solution a success in EU table olive sector.
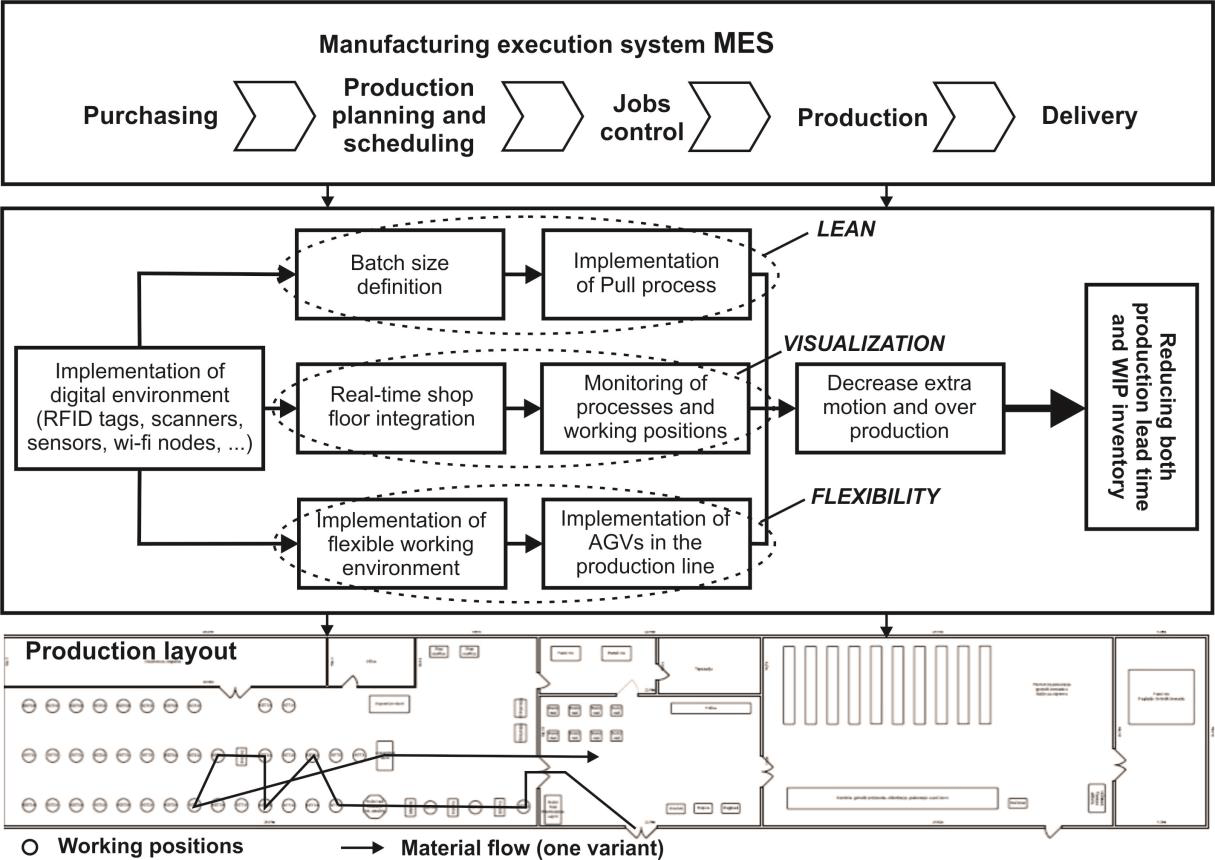
The solution consists of AGVs which will provide required flexibility and interconnectivity in the production system. AGVs will be controlled by the ROS and IR sensors for starting/stopping. The optimal number and specific characteristics of AGVs will be the results of a conceptual solution developed by DIH (simulation model) and practically realized by a subcontracted party. RFID system for the material flow visualization will be used to monitor material flows (in batches) in the production system and enable real-time information gathering in a database. Custom-built MES solution will serve for the operational production scheduling/balancing in terms of human workload, working stations (interconnected by AGVs) and time.
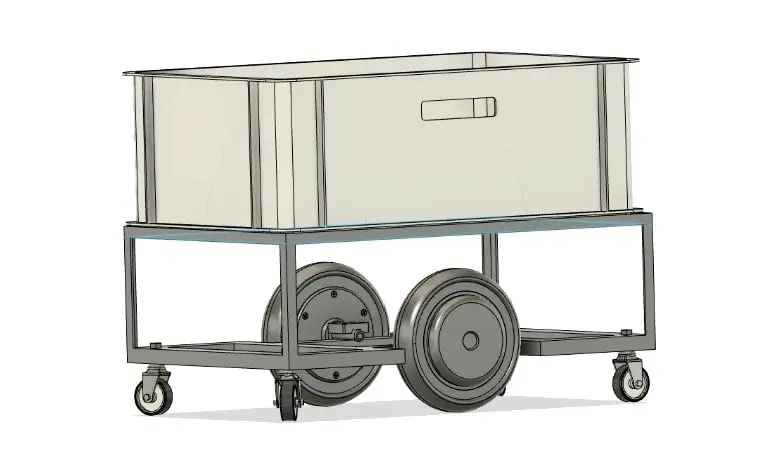
AGV model planned to be implemented in production process
